Welcome to the official website of Hebei Ruihua Metallurgical Technology Co., Ltd.!
Welcome to the official website of Hebei Ruihua Metallurgical Technology Co., Ltd.!
Reducing slag during the converter tapping process is a key aspect of improving molten steel quality. Low-slag or slag-blocking tapping is essential for producing pure steel. Its purpose is to accurately control the molten steel composition, effectively reduce rephosphorization, increase alloying element absorption, and reduce alloy consumption. This helps reduce inclusion content in the steel, improve ladle refining efficiency, and reduce corrosion of the ladle’s refractory materials, extending the ladle’s service life. It also improves the life of the converter tapping port. Currently, off-furnace refining requires a ladle slag layer thickness of less than 50 μm and a slag volume of less than 3 kg/ton of steel.
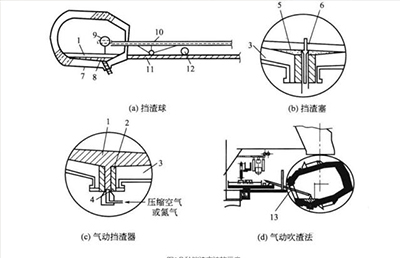
Since the invention of the slag ball tapping method in Japan in 1970, slag blocking technology has continued to advance. Currently, there are over a dozen slag blocking methods, including the slag cap method for primary slag blocking; slag balls, slag plugs, slag rods, slag shields, electromagnetic slag blocking, pneumatic slag blockers, and pneumatic slag blowing methods for secondary slag blocking, as shown in Figure 1.
(1) Slag stopper cap
A conical slag stopper cap made of steel plate is placed outside the tapping port to block the slag at the beginning of tapping.
(2) Slag stopper ball
The density of the slag stopper ball is between that of molten steel and slag (generally 4.2~4.5g/cm3). It is placed near the tapping port near the end of tapping. As the molten steel level drops, the slag stopper ball sinks and blocks the tapping port, preventing the slag from entering the ladle. Considering that the tapping port becomes larger due to erosion, the diameter of the slag stopper ball should be slightly larger than the tapping port diameter to play the role of slag stopper.
(3) Slag stopper plug
The slag stopper plug can effectively prevent slag from entering the steel flow. The structure of the slag stopper consists of a plug rod and a plug head. Its material is the same as that of the slag stopper ball, and its density can be the same as or slightly lower than that of the slag stopper ball. The upper part of the plug rod is a steel rod used for clamping and positioning, and the lower part is wrapped with refractory material. When tapping is about to end, the plug rod is inserted into the tapping port by mechanical loading according to the tapping angle of the converter and in strict alignment. When tapping is finished, the plug seals the tapping port. There are grooves on the plug head, through which the remaining molten steel in the furnace can flow out, while the slag is blocked in the furnace. The slag stopper has the dual functions of blocking slag and suppressing vortexes. It is more effective than the slag ball in blocking slag and is currently widely used.
(4) Slag hood
It was invented by the Alledron Steel Company in the United States in 1988. The slag hood is built at the tapping port. When tapping, the molten steel flows into the tapping port through the side holes of the slag hood made of refractory material. Since the top of the slag hood is closed, it hinders the conditions for the formation of vortexes above the tapping port, which can effectively prevent vortex slag from entraining.
(5) Pneumatic slag stopper
When tapping is about to end, a mechanical device blows air into the tapping port from the outside of the converter using the slag stopper nozzle to prevent the slag from flowing out. This method has strict requirements on the shape and position of the tapping hole, and requires the nozzle to be aligned with the center line of the tapping hole.
(6) Pneumatic slag blowing method
It is very difficult to block the slag under the vortex in the late stage of tapping. Once the vortex is generated, it is easy for the slag and steel to mix. Therefore, in order to prevent the generation of vortex in the late stage of tapping, or even if vortex is generated, the most effective method is to block the slag on the surface of the vortexing molten steel. This is the pneumatic slag blowing method. High-pressure gas is used to blow away and block the slag on the molten steel surface above the tapping hole to achieve the purpose of slag removal. This method can reduce the slag layer thickness of the ladle to 15~55mm.